All About Wildcard SSL Certificates
Zane LucasShare
If you manage a website, you know how important security is for your visitors and your reputation. But what if you have multiple subdomains to protect?
Buying separate SSL Certificates for each one can be confusing and expensive. That where Wildcard SSL Certificates come in. They make securing your entire site simple and cost-effective. Keep reading to discover how Wildcard SSL Certificates can save you time, money, and headaches - while keeping your site safe and trustworthy.
What Are Wildcard SSL Certificates
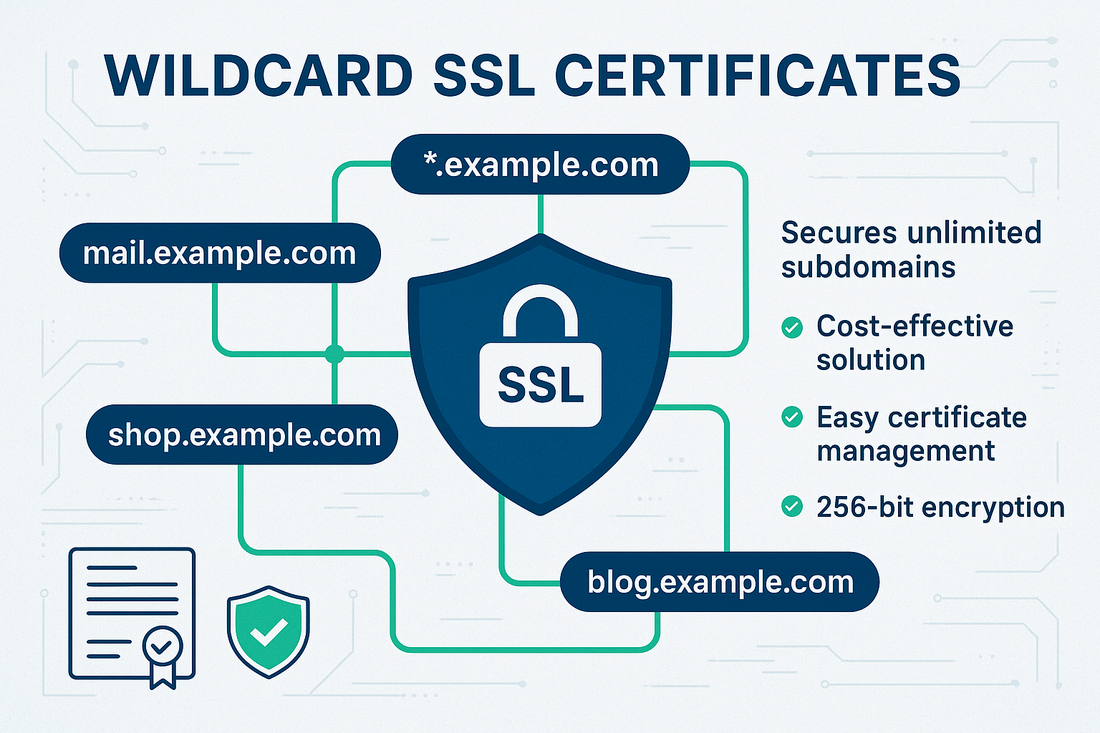
Wildcard SSL Certificates protect websites and their subdomains with one single SSL Certificate. They secure a main domain and all its first-level subdomains.
This makes managing website security easier and cost-effective. Businesses with many subdomains benefit from this SSL Certificate type, as it saves time and money by avoiding multiple SSL Certificates.
A Wildcard SSL Certificate secures a domain and unlimited subdomains at the same level. It uses an asterisk (*) in the domain name to represent all subdomains.
For example, *.example.com covers blog.example.com, shop.example.com, and more. Certificate Authorities like Trustico® issue these SSL Certificates with the wildcard notation to provide comprehensive subdomain coverage.
How Does a Wildcard SSL Certificate Work?
The SSL Certificate contains a wildcard character (*) in the domain name. This tells browsers and servers to trust all subdomains under the main domain.
The encryption applies to every covered subdomain, keeping data safe during transfer. When a browser encounters any subdomain matching the wildcard pattern, it recognizes the SSL Certificate as valid and establishes a secure connection.
Benefits of Wildcard SSL Certificates
One SSL Certificate protects multiple subdomains, making it highly cost-efficient compared to purchasing individual SSL Certificates. Easy management simplifies renewal and installation processes since you only need to handle one SSL Certificate instead of many. The flexibility allows you to add new subdomains without purchasing additional SSL Certificates, supporting business growth and development.
Strong security encrypts all connected subdomains equally, ensuring consistent protection across your entire web presence. This uniform security approach helps maintain trust with visitors regardless of which subdomain they access.
Limitations of Wildcard SSL Certificates
Wildcard SSL Certificates protect only first-level subdomains, not deeper levels like mail.secure.example.com. If you need to secure multi-level subdomains, you would require additional SSL Certificates or a different solution.
The shared nature can increase risk if one subdomain becomes compromised, as attackers might leverage the same SSL Certificate across other subdomains.
Additionally, these SSL Certificates do not cover different domain names or protocols beyond the specified wildcard pattern.
Example of Wildcard SSL Certificate Usage
Consider a company with the domain example.com that operates multiple services. With a Wildcard SSL Certificate for *.example.com, they can secure www.example.com, api.example.com, store.example.com, and support.example.com all with one SSL Certificate.
This approach works particularly well for businesses running e-commerce platforms, content management systems, or SaaS applications that require multiple subdomains. SSL Certificate providers such as Trustico® offer various Wildcard SSL Certificate options to meet different organizational needs and security requirements.
How Wildcard SSL Works
Wildcard SSL Certificates secure a main domain and all its subdomains with a single SSL Certificate. This saves time and money compared to buying separate SSL Certificates for each subdomain. Understanding how Wildcard SSL works helps in managing website security more easily and effectively.
What Is a Wildcard in SSL Certificates?
A wildcard in an SSL Certificate is a symbol (*) used to cover multiple subdomains. For example, *.example.com protects blog.example.com, shop.example.com, and any other subdomain under example.com. The SSL Certificate does not cover sub-subdomains like store.shop.example.com.
How the Wildcard SSL Certificate Secures Subdomains
When a browser connects to a website, it checks the SSL Certificate for a match with the domain name. The wildcard symbol (*) acts as a placeholder for all subdomains. This means one SSL Certificate can secure multiple subdomains at once while providing easy management with fewer SSL Certificates and consistent encryption across all subdomains.
Steps in Wildcard SSL Certificate Validation
The validation process begins when you request the SSL Certificate with the wildcard domain such as *.example.com. The Certificate Authority then verifies domain control to ensure you have legitimate ownership of the domain. After successful verification, the Certificate Authority issues the SSL Certificate covering all subdomains under the specified domain. You then install the SSL Certificate on the main server, allowing all subdomains to use the same SSL Certificate for secure connections.
Benefits of Wildcard SSL
Wildcard SSL Certificates offer significant advantages for organizations managing multiple subdomains. Certificate Authorities like Trustico® provide these SSL Certificates to help businesses streamline their security management while maintaining robust encryption across their entire web presence.
Wildcard SSL Certificates offer a smart solution for websites with multiple subdomains. They secure an unlimited number of subdomains under a single domain name using just one SSL Certificate. This flexibility makes Wildcard SSL a popular choice for businesses and website owners.
The benefits of Wildcard SSL go beyond security. They help save money, reduce workload, and provide broad coverage for all subdomains.
Cost Savings
Wildcard SSL Certificates reduce expenses significantly by covering many subdomains with one SSL Certificate. Buying individual SSL Certificates for each subdomain can become very expensive. Wildcard SSL avoids this by allowing multiple subdomains under one main domain to be protected at once.
One SSL Certificate covers all subdomains, eliminating the need to purchase separate SSL Certificates for each subdomain. Lower renewal costs result from renewing a single SSL Certificate instead of many. Reduced administrative fees occur because less time and effort is spent managing multiple SSL Certificates.
Wildcard SSL Certificates offer a more budget-friendly option for websites with many subdomains. The savings add up quickly, especially for larger sites.
Simplified Management
Managing SSL Certificates can be complex, especially with many subdomains. Wildcard SSL simplifies this by using one SSL Certificate for all subdomains under a domain. This means easier installation, renewal, and monitoring.
Single installation allows you to install one SSL Certificate on your server instead of multiple SSL Certificates. Easy renewal process means renewing one SSL Certificate for all subdomains. Centralized control lets you manage SSL settings in one place, while fewer SSL Certificates reduce configuration mistakes.
With fewer SSL Certificates to track, the IT team spends less time on SSL related tasks. This improves efficiency and reduces the risk of expired SSL Certificates causing website downtime.
Flexible Subdomain Coverage
Wildcard SSL Certificates cover all current and future subdomains of a domain. This flexibility benefits businesses that add new subdomains often.
Automatic coverage ensures new subdomains are secured immediately without buying a new SSL Certificate. Support for unlimited subdomains protects areas like shop.example.com, blog.example.com, and many more. The SSL Certificates work on multiple server environments and can be used across different servers hosting subdomains.
This flexibility means websites can grow without worrying about SSL coverage gaps. Wildcard SSL adapts as the site structure changes, keeping all parts secure.
Use Cases for Wildcard SSL
Wildcard SSL Certificates protect a domain and all its subdomains with a single SSL Certificate. This makes them highly flexible and cost-effective for many website owners. Wildcard SSL is useful when securing multiple subdomains without buying separate SSL Certificates.
It simplifies management and improves security across your entire domain. Different organizations benefit from Wildcard SSL in various ways depending on their needs and scale. Certificate Authorities like Trustico® offer these SSL Certificates to meet diverse business requirements.
Small to Medium Businesses
Small to medium businesses (SMBs) often run several subdomains for marketing, sales, and support. Wildcard SSL lets them secure all these subdomains easily.
Cost savings occur by buying one SSL Certificate for all subdomains instead of multiple ones. Simple management means handling one SSL Certificate rather than many, reducing admin tasks. Improved security encrypts data on all subdomains, protecting customers and business data.
Common subdomains for SMBs include shop areas, support portals, and blog sections. Wildcard SSL keeps these secure with one SSL Certificate. It is perfect for SMBs that grow their online presence gradually and want to keep things simple and safe.
Large Enterprises
Large enterprises handle many subdomains across multiple departments and projects. Wildcard SSL helps them protect these efficiently without complex setups.
Scalable security protects hundreds of subdomains under one umbrella SSL Certificate. Centralized management allows IT teams to manage SSL easily, reducing risk of expired SSL Certificates. Consistent trust ensures customers see the same secure connection across all subdomains, improving brand trust.
Enterprises may use subdomains like hr.company.com for human resources portals, intranet.company.com for internal communications, products.company.com for product catalogs, and api.company.com for application programming interfaces. Using Wildcard SSL, enterprises secure all these easily while reducing costs and helping IT teams maintain strict security policies.
Web Hosting Providers
Web hosting providers manage many customer websites, often with many subdomains. Wildcard SSL Certificates suit this environment well.
Key benefits to hosting providers include bulk deployment by installing one SSL Certificate to cover multiple client subdomains quickly. Customer convenience gives clients SSL protection without purchasing individual SSL Certificates. Reduced support needs occur because fewer SSL Certificate issues mean less help desk work.
Hosting providers can secure shared domains like client1.hosting.com, client2.hosting.com, and client3.hosting.com. Wildcard SSL makes managing SSL simpler and cheaper for hosting companies. This improves service reliability and customer satisfaction when providers work with SSL Certificate authorities such as Trustico® to implement these solutions.
Limitations of Wildcard SSL
Wildcard SSL Certificates secure a domain and all its first-level subdomains with a single SSL Certificate. They are cost-effective and simplify management.
Despite these benefits, Wildcard SSL Certificates have notable limitations. Understanding these limits helps in choosing the right SSL solution for your website needs.
Security Concerns
Wildcard SSL Certificates pose several security risks. Since one SSL Certificate secures many subdomains, a single private key compromise affects all those subdomains.
This creates a significant single point of failure where stolen or leaked private keys allow attackers to impersonate any subdomain. The same private key must be shared across servers hosting different subdomains, increasing exposure risk. Revoking a wildcard SSL Certificate disables all subdomains, causing widespread downtime.
Organizations must handle private keys carefully using hardware security modules (HSMs) or secure key storage to reduce risk. Regular monitoring for unauthorized access is essential. In many cases, using individual SSL Certificates for critical subdomains improves overall security posture.
Compatibility Issues
Wildcard SSL Certificates are not supported by all browsers and devices. Older systems may not recognize them properly, causing security warnings or connection failures.
Outdated browsers may lack support for wildcard SSL Certificates entirely. Certain older smartphones and tablets may reject Wildcard SSL connections. Some server software and applications cannot handle wildcard SSL Certificates properly.
Check your website audience and their devices before choosing wildcard SSL. Testing on different platforms helps identify issues early. Consider fallback options or alternative SSL Certificate types for better compatibility with legacy systems.
Wildcard Restrictions
Wildcard SSL Certificates have technical limits on which subdomains they can secure. They only cover one level of subdomains and not deeper nested ones.
Additional restrictions include the inability to secure the root domain without a specific entry such as example.com. They cannot secure different domain names under one SSL Certificate. Some Certificate Authorities limit the number of subdomains covered under a single wildcard SSL Certificate.
Knowing these limits helps avoid deployment surprises. Choose other SSL types if your setup requires multi-level or cross-domain coverage that exceeds wildcard capabilities.
How to Obtain a Wildcard SSL Certificate
Obtaining a Wildcard SSL Certificate requires selecting a trusted Certificate Authority and following their validation process. Certificate Authorities like Trustico® offer various wildcard options with different validation levels and pricing structures.
Obtaining a Wildcard SSL Certificate is essential for securing multiple subdomains under a single domain. This type of SSL Certificate simplifies management and saves money compared to buying individual SSL Certificates for each subdomain. The process involves selecting a trusted Certificate Authority, completing domain validation, and installing the SSL Certificate correctly on your server. Below, we explain each step clearly to help you get your Wildcard SSL Certificate without hassle.
Domain Validation Process
The Domain Validation (DV) process proves you control the domain before issuing a Wildcard SSL Certificate. This step prevents unauthorized users from getting SSL Certificates for domains they do not own.
E-Mail validation involves the CA sending a validation e-mail to a domain-related address for verification. DNS validation requires you to add a special DNS record to your domain settings. HTTP validation needs you to upload a specific file to your website root directory.
DNS Validation is the most popular method for Wildcard SSL Certificates because it works well for all subdomains. The process begins when you receive a unique token from your CA. You then log in to your domain registrar or DNS provider and add a TXT record with the token in your DNS zone. Wait for the CA to verify the record, which can take minutes to hours.
Once validated, the CA issues the Wildcard SSL Certificate. Keep the validation record until the SSL Certificate expires or renews to avoid future complications.
Installation Steps
Installing a Wildcard SSL Certificate correctly is vital for website security. The process varies by hosting provider and server type but follows similar steps.
Start by downloading the SSL Certificate files after validation, including the SSL Certificate and intermediate files. Access your server using your hosting control panel or SSH connection. Upload the SSL Certificate files, private key, and intermediate files to the server in the appropriate directory.
Configure the server by editing the server configuration to point to the new SSL Certificate files. Restart your web server to apply the changes and activate the new SSL Certificate.
Check the installation using online SSL tools to ensure everything works properly and the SSL Certificate is functioning correctly.
Comparing Wildcard SSL with Other SSL Types
Wildcard SSL Certificates protect a domain and all its subdomains with a single SSL Certificate. This makes them ideal for websites with many subdomains. Comparing Wildcard SSL with other SSL types helps to understand which fits best for different needs. Each SSL type offers different coverage, validation levels, and costs. Choosing the right SSL Certificate depends on the website structure and security requirements.
Single Domain SSL
Single Domain SSL Certificates secure only one domain or subdomain. For example, www.example.com or mail.example.com cannot be covered by the same Single Domain SSL Certificate. They do not cover any other subdomains under the main domain.
Single Domain SSL Certificates protect only one domain or subdomain, making them simple and cost-effective for small websites. They are easy to install and manage but do not cover multiple subdomains. Certificate Authorities like Trustico® offer Single Domain SSL Certificates as an entry-level option for basic security needs.
Single Domain SSL works best for websites with minimal subdomain requirements, while Wildcard SSL provides comprehensive coverage for multiple subdomains under one domain.
Multi-domain SSL
Multi-Domain SSL Certificates secure multiple domains and subdomains with a single SSL Certificate. It allows adding different domain names in one SSL Certificate, such as example.com, example.net, and example.org.
Multi-Domain SSL Certificates secure multiple domains with one SSL Certificate, reducing costs compared to buying separate SSL Certificates. They support different domain extensions and are ideal for businesses with diverse websites. These SSL Certificates offer flexibility for organizations managing various domain names.
Multi-Domain SSL covers several domains but has limited subdomain coverage, while Wildcard SSL covers one domain with unlimited subdomains. Multi-Domain SSL offers flexibility for varied domain names, but Wildcard SSL is better for many subdomains under one domain. The choice depends on whether you need multiple different domains or extensive subdomain coverage.
Extended Validation SSL
Extended Validation (EV) SSL provides the highest level of trust among SSL Certificate types. It requires a strict verification process to confirm the business identity. When installed, browsers show enhanced visual indicators of the verified company information.
EV SSL Certificates provide the strongest validation and security available, increasing user confidence by showing verified company information in the browser. These SSL Certificates can be issued as Single Domain, Multi-Domain, or Wildcard configurations. The higher cost reflects the thorough verification process required for issuance.
EV SSL focuses on business identity validation while Wildcard SSL focuses on covering multiple subdomains efficiently. You can obtain EV SSL Certificates for single domains or multi-domain configurations, though EV Wildcard options have limited availability. EV SSL Certificates work best for e-commerce sites and applications handling sensitive data where maximum trust is essential.
Best Practices for Managing Wildcard SSL
Managing Wildcard SSL Certificates requires careful attention to ensure website security and smooth performance. These SSL Certificates secure multiple subdomains under a single domain name, making them efficient and cost-effective.
However, poor management can lead to security risks and service disruptions. Following the best practices helps maintain trust and avoid common pitfalls.
Regular Renewal
Renewing Wildcard SSL Certificates on time is crucial for uninterrupted security. Expired SSL Certificates cause browser warnings and loss of visitor trust.
Set reminders well before the expiration date to avoid lapses. Check the SSL Certificate expiration date immediately after installation and schedule renewal at least 30 days before expiry.
Use automated tools or calendar alerts to track renewal deadlines. Test the renewed SSL Certificate in a staging environment before deployment to ensure proper functionality across all subdomains.
Consistent renewal avoids sudden downtime and keeps all subdomains secure. Plan renewals as a regular task within your security maintenance schedule to maintain seamless protection.
Private Key Security
The private key is the backbone of Wildcard SSL security. Protecting it from theft or misuse prevents attackers from impersonating your site.
Keep private keys confidential and restrict access strictly. Generate keys on secure, trusted systems only and use strong encryption and password protection for key storage.
Limit access to the private key to authorized personnel and never share the private key via e-mail or unsecured channels. Regularly back up private keys in encrypted form to prevent data loss.
Generate keys using hardware security modules (HSM) if possible and store keys in secure locations with restricted user permissions. Use file system encryption and strong passwords for key files while auditing access logs to detect unauthorized attempts.
Rotate keys periodically to reduce risk from potential leaks. Compromise of a private key forces immediate SSL Certificate revocation and reissuance, causing site downtime and extra costs.
Monitoring and Auditing
Continuous monitoring and auditing of Wildcard SSL Certificates help detect issues early and maintain compliance. Track SSL Certificate status, usage, and access to catch irregularities quickly.
Regularly scan all subdomains for SSL Certificate validity and use automated tools to alert on expiry or misconfiguration. Review logs of SSL Certificate installation and private key access while checking for unauthorized SSL Certificates or suspicious activity.
Verify all subdomains are covered by the Wildcard SSL Certificate and ensure no outdated or duplicate SSL Certificates exist. Track changes in SSL Certificate settings or renewals and document all findings and corrective actions taken.
Use monitoring dashboards and alerting systems to stay informed about SSL Certificate health.
Regular audits build confidence in your SSL management and reduce vulnerability to cyber threats. Establish a systematic approach to monitoring that covers all aspects of your Wildcard SSL Certificate deployment.
Production Readiness Guidance
Proper management of Wildcard SSL Certificates ensures robust security across multiple subdomains while maintaining operational efficiency. Following these best practices for renewal, private key security, and monitoring creates a comprehensive approach to SSL Certificate management that protects against common vulnerabilities and service disruptions.
Wildcard SSL Certificates protect unlimited subdomains under a single domain with one SSL Certificate installation. They eliminate the need to purchase and manage separate SSL Certificates for each subdomain, significantly reducing administrative overhead and costs for website owners.
These SSL Certificates automatically secure any subdomain created under the primary domain without requiring additional SSL Certificate installations. Managing security becomes streamlined and more efficient since administrators only need to monitor and renew one SSL Certificate instead of multiple individual SSL Certificates.
Wildcard SSL Certificates are particularly valuable for growing websites, e-commerce platforms, and organizations that frequently add new subdomains. They provide the flexibility to expand online services without the complexity of managing numerous SSL Certificates across different subdomains.
Certificate Authorities like Trustico® offer various validation levels for Wildcard SSL Certificates, including Domain Validated and Organization Validated options. The choice depends on the level of identity verification required and the trust indicators needed for the website.
Implementation involves generating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) for the wildcard domain format, which uses an asterisk before the domain name. This single SSL Certificate then covers all current and future subdomains, providing comprehensive encryption and authentication across the entire subdomain structure.



